MileBot Robotics provides innovative rehabilitation solutions for Stroke recovery. Our product offerings include the Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot BEAR (H Series), BEAR (A Series), RELAX (C Series), and Gait Assist Systems MAX (M and F Series). These devices are designed to support neuroplasticity and enhance mobility, offering personalized therapy to meet the specific needs of stroke patients. Our advanced technology ensures effective rehabilitation, promoting faster recovery and improved quality of life.
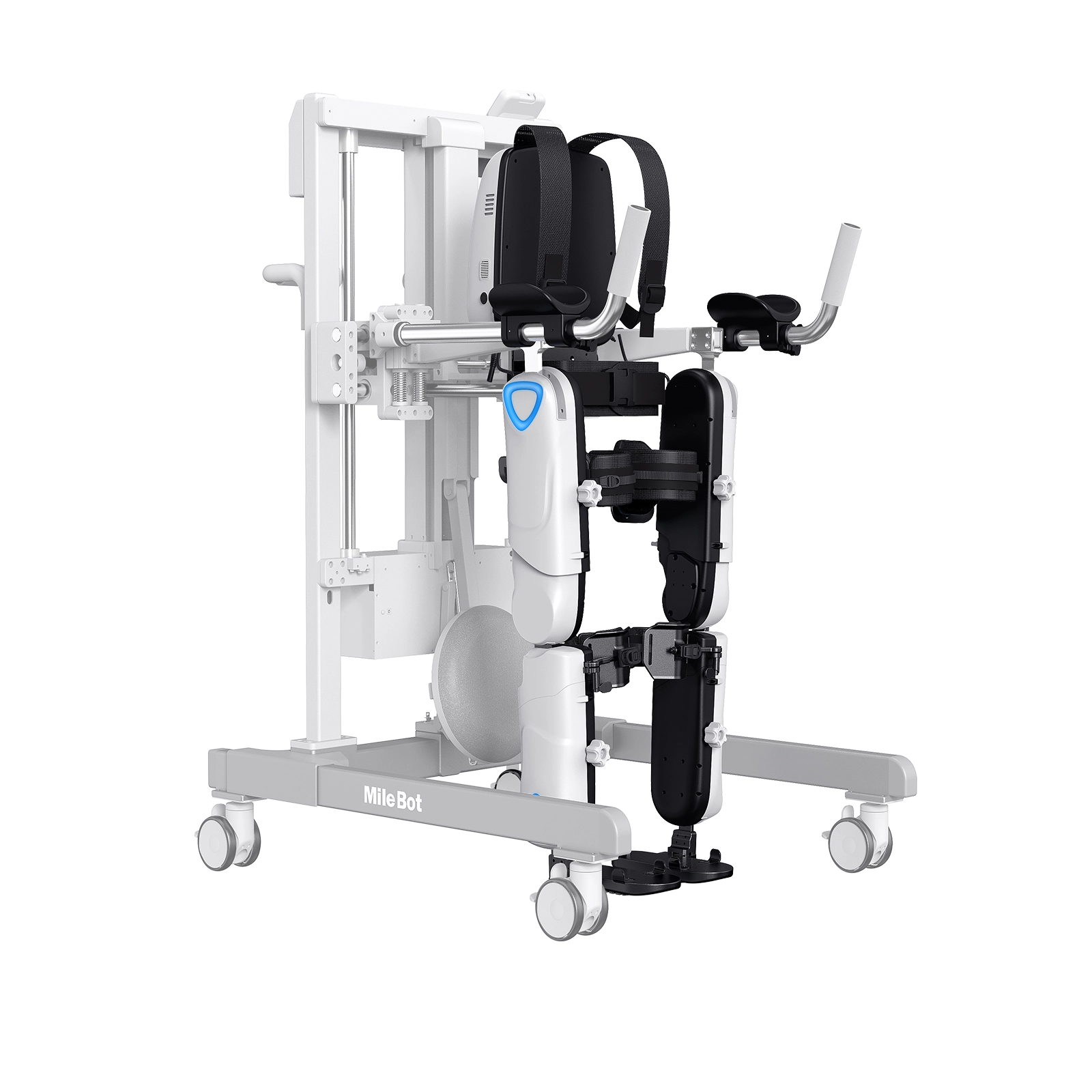
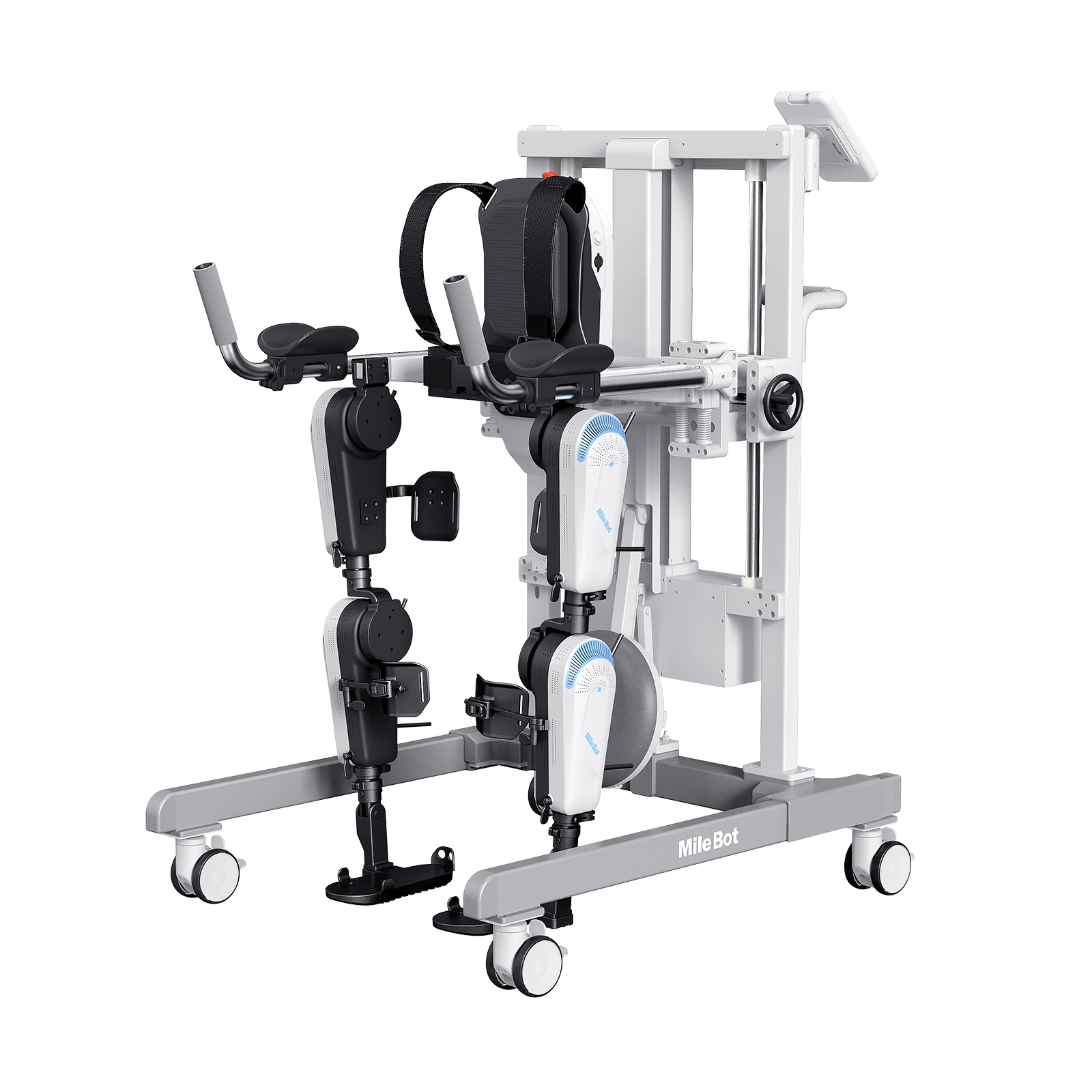
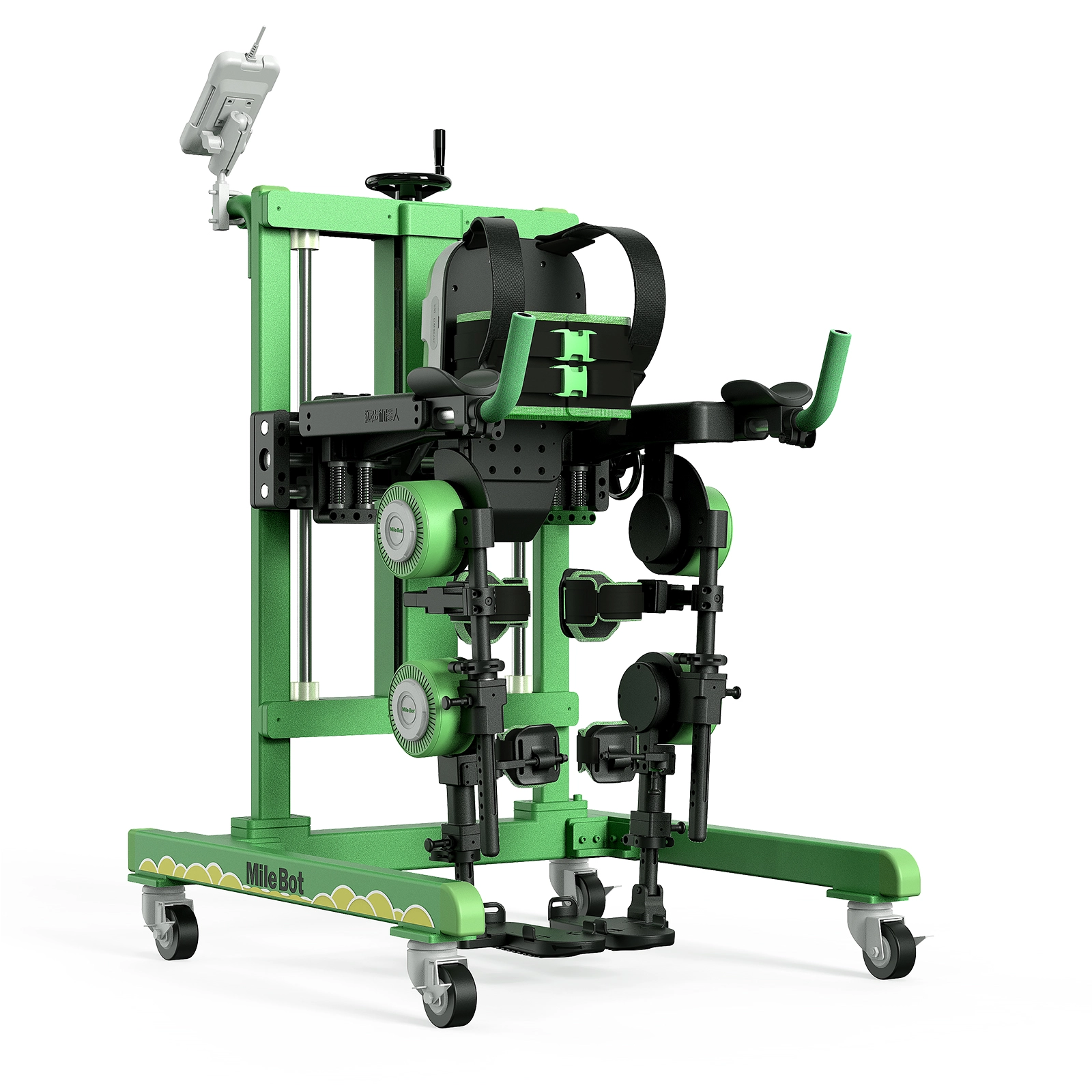
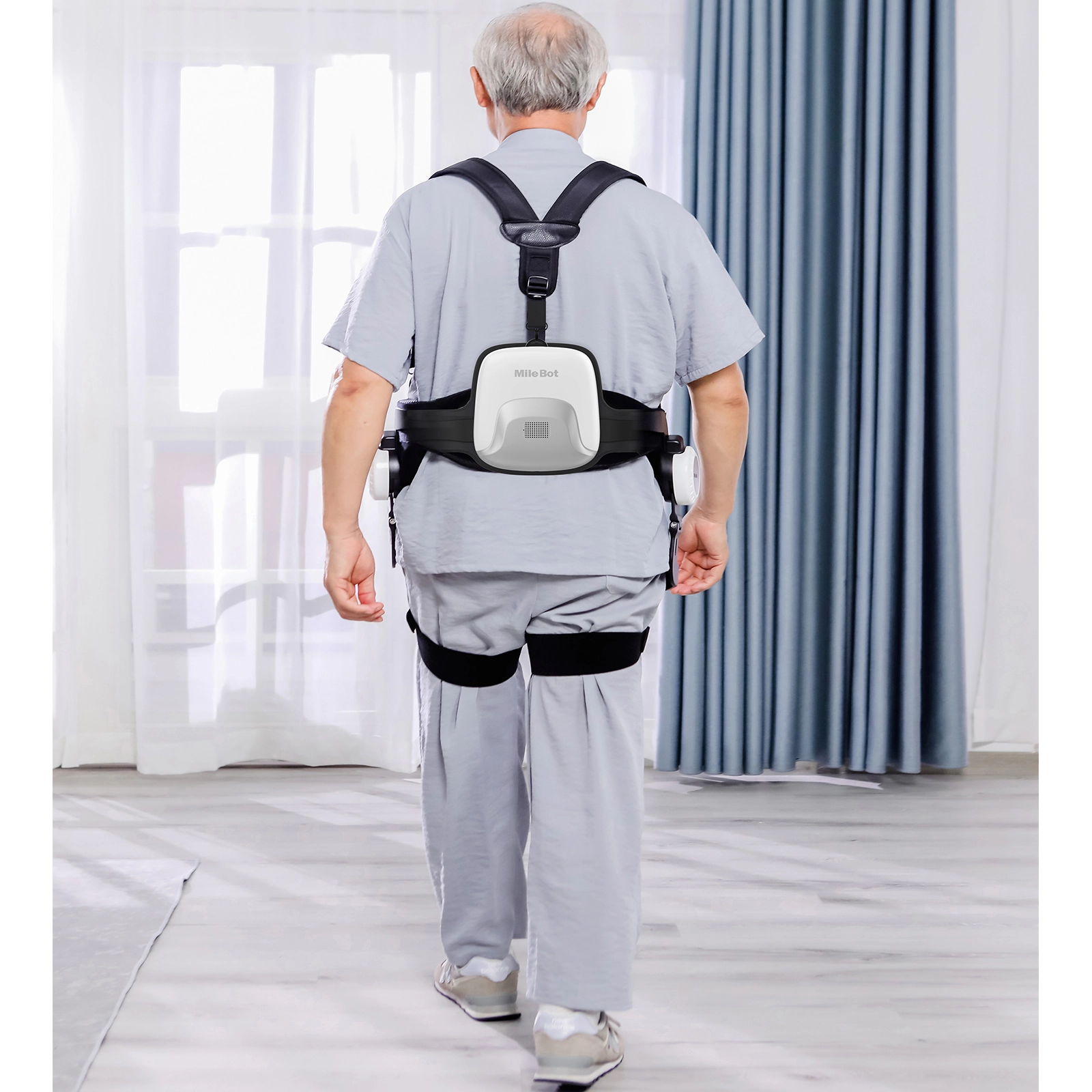




Stroke rehabilitation is a critical process aimed at helping patients regain lost functions and improve their quality of life. Traditional methods often involve physical therapy, but advancements in technology are offering new, personalized approaches.
Robotic exoskeletons are wearable devices designed to support and enhance the user's natural movements. These devices are equipped with sensors, actuators, and advanced algorithms to assist in walking and other motor functions.
The future of personalized stroke rehabilitation looks promising with ongoing advancements in medical robotics. As technology continues to evolve, robotic exoskeletons are expected to become more accessible and effective, revolutionizing stroke recovery.
Stroke is a leading cause of disability worldwide, and effective rehabilitation is crucial for recovery. Traditional rehabilitation methods have limitations, prompting the exploration of innovative solutions like robotic exoskeletons.
Clinical Trials and Studies: Numerous clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of robotic exoskeletons in stroke rehabilitation. These studies focus on various aspects, including mobility improvement, muscle strength, and neuroplasticity.
Technological Advancements: Recent advancements in medical robotics have led to the development of more sophisticated exoskeletons. These devices are equipped with advanced sensors, actuators, and machine learning algorithms to provide personalized therapy.
Patient Outcomes: Early research indicates that patients using robotic exoskeletons show significant improvements in mobility, muscle strength, and overall quality of life. These devices also offer psychological benefits by boosting confidence and independence.
Enhanced Mobility: Robotic exoskeletons can significantly improve mobility for stroke patients. By supporting and augmenting natural movements, these devices help patients walk more easily and with better coordination.
Muscle Strength and Endurance: Regular use of exoskeletons can improve muscle strength and endurance, which are often compromised in stroke patients. This leads to better overall physical health and reduced fatigue.
Neuroplasticity: Robotic exoskeletons promote neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This is crucial for stroke recovery, as it helps patients regain lost functions.
Accessibility and Cost: One of the main challenges is the high cost of robotic exoskeletons, which can limit accessibility for many patients. However, ongoing research and development are expected to make these devices more affordable and widely available.
Customization and Adaptability: Future advancements aim to create more customizable and adaptable exoskeletons that can meet the specific needs of individual stroke patients. This will make the devices even more effective in rehabilitation.
Integration with Traditional Therapy: Combining robotic exoskeletons with traditional rehabilitation methods can offer a synergistic approach, enhancing the overall effectiveness of stroke therapy.
Robotic exoskeletons are revolutionizing stroke rehabilitation by offering enhanced mobility, muscle strength, and neuroplasticity. Current research shows promising results, and future advancements are expected to make these devices more accessible and effective. As technology continues to evolve, robotic exoskeletons will play an increasingly important role in stroke recovery, offering new hope for patients worldwide.
Exoskeletons help by supporting and enhancing natural movements, aiding in the recovery of motor functions affected by stroke.
The timing can vary, but early intervention is often recommended to maximize recovery potential.
Risks can include skin irritation, muscle fatigue, and mechanical failure, but these are generally rare and can be managed with proper supervision and maintenance.